Abdelrahman Elhakim1*, Mohamed Gayed2, Mohamed Elhakim3 and Mohamed Saad4
1Interventional Cardiology Consultant, Schoen Hospital Neustadt, Am Kiebitzberg 10, Neustadt in Holstein, Germany
2Interventional Cardiologist, Medinos Hospital Sonneberg, Neustadter Street 61, Sonneberg, Germany
3Critical Care and Anesthesia Medical Officer, Nepean Hospital, Derby Street, Kingswood NSW, Sydney, Australia
4Interventional Cardiology Consultant, Schleswig-Holstein University Hospital-Kiel, Arnold-Heller-Street 3, Kiel, Germany
*Corresponding author: Abdelrahman Elhakim, Interventional Cardiology Consultant, Schoen Hospital Neustadt, AM Kiebitzberg 10, 23730, Neustadt in Holstein, Germany.
Received: May 14, 2023; Accepted: May 26, 2023; Published: July 05, 2023
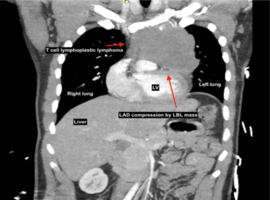
Citation: Elhakim A, Gayed M, Elhakim M, Saad M. Adult T-type Lymphoblastic Lymphoma Presenting as Inferior Wall Myocardial Infarction: A Case Report. Case Rep Clin Cardiol J. 2023; 3(3): 131.